Vaccination of children in Russia is carried out according to a certain schedule, which is called the vaccination calendar. Our national vaccination calendar is one of the most comprehensive in the world. It is approved at the legislative level and is used throughout the country. In addition to routine vaccinations, there are vaccinations for epidemic indications that are given in some regions when an epidemic threat occurs.
Despite the thoroughness of the vaccination calendar, vaccinations are not required. Parents may well refuse to vaccinate the child by providing a written refusal. Read more about the vaccination schedule, vaccines and vaccination rules, as well as about refusing it, read below.
What laws regulate vaccination of children
There are several laws behind the development of a vaccination calendar and vaccination of children:
- Federal Law “On the Immunoprophylaxis of Infectious Diseases”.
- "Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on the protection of the health of citizens."
- The law of the Russian Federation “On the sanitary-epidemiological well-being of the population”.
These documents prescribe the entire vaccination procedure, including a list of recommended vaccinations and possible complications after them. So, vaccination of children up to a year implies vaccination against the following diseases:
- Viral hepatitis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Whooping cough;
- Diphtheria;
- Tetanus;
- Hemophilic infection;
- Polio;
- Measles;
- Rubella;
- Mumps.
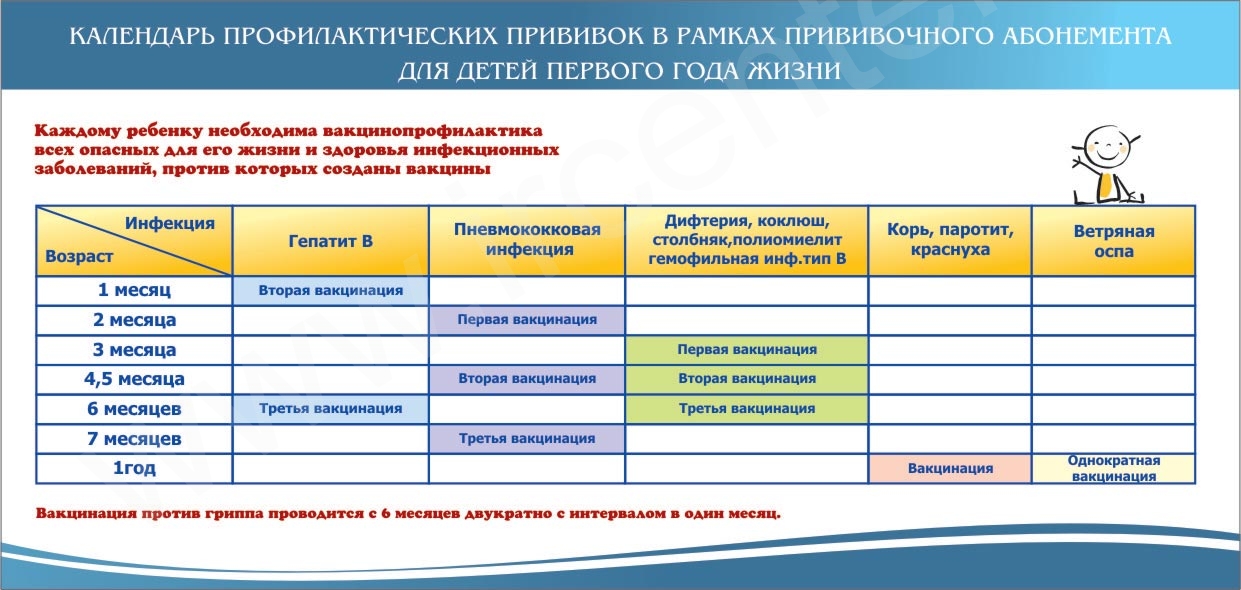
National vaccination calendar for children under one year old
Every year, the vaccination calendar changes a little, some additions are made to it. Basically, they relate to the procedure for vaccination, and the vaccination schedule remains the same:
| Age | Vaccination name | Vaccine | Notes |
| 1 day (newborn) | - The first vaccine against viral hepatitis B | Angerix B, Combiotech | Especially necessary for newborns whose mothers are carriers of the virus or are sick with acute or chronic hepatitis. |
| 3-7 days (newborn) | - Vaccination against tuberculosis | BCG-M | Not to be confused with the Mantoux reaction. Mantoux is not a vaccination, but an analysis of the presence of immunity, it is carried out after a year. If there is no immunity, BCG vaccine is repeated. |
| Baby in 1 month | - Second hepatitis B vaccine | Angerix B, Combiotech | |
| Baby in 2 months | - Third hepatitis B vaccine | Angerix B, Combiotech | It is put only to children at risk. |
| 3 months baby | - First vaccination for pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus | DTP, Infanrix, Pentaxim | Each vaccine has its own vaccine, but all 3 vaccinations can be delivered “in one shot” if you use the Pentaxim combination vaccine. |
| - The first vaccination against hemophilic infection | Act-HIB, Hiberix, Pentaxim | ||
| - First polio vaccine | OPV, IPV, Pentaxim | ||
| Baby at 4.5 months | - Second vaccination for pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus | DTP, Infanrix, Pentaxim | |
| - The second vaccination against hemophilic infection | Act-HIB, Hiberix, Pentaxim | ||
| - Second polio vaccine | OPV, IPV, Pentaxim | ||
| Baby at 6 months old | - Third vaccination for pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus | DTP, Infanrix, Pentaxim, Bubo-Kok | The vaccine against pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus can be given “in one shot” with the hepatitis vaccine if you use the Bubo-Kok combination vaccine. |
| - The third vaccination against hemophilic infection | Act-HIB, Hiberix, Pentaxim | ||
| - Third polio vaccine | OPV, IPV, Pentaxim | ||
| - Third hepatitis B vaccine | Angerix B, Combiotech, Bubo Kok | ||
| 12 months baby | - Vaccination against measles, rubella and mumps | MMR II, Priorix | |
| - Fourth hepatitis B vaccine | Angerix B, Combiotech | Only for at-risk babies. |
About vaccines
Up to a year, the child will have to get 14 vaccinations (taking into account the fact that some vaccinations are given in several stages), and mothers will need to find out many names of vaccines and decide which vaccine to give the child. Let's try to figure out what vaccines are.
- Hepatitis B vaccine. It contains individual proteins of the hepatitis B virus. There is no genetic material for the virus. In response to the introduction of the vaccine, immunity is formed, it is impossible to get sick in this way.
- Tuberculosis vaccine. Contains weakened bovine tuberculosis bacteria. In humans, they do not cause disease, but lead to the formation of stable immunity. For the development of stable immunity, it is necessary that the tubercle bacillus is constantly in the body.
- Vaccine for pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus. The most severe in these diseases is the poisoning of the body with toxins. The vaccine contains precisely toxins, but in a very weakened form. They do not cause disease, but the body produces immunity.
- Polio vaccine. There are two types: living and inactivated. A live vaccine is directly a polio virus in a very weakened form. This vaccine is available in the form of drops and can cause mild polio in a child. An inactivated vaccine contains only protein coatings of viruses. It is administered subcutaneously, can not cause the disease, but the effect of it is lower. Since the polio vaccine is given in 2 stages, sometimes an inactivated vaccine is given first and the second vaccine is made live.
- The measles, rubella and mumps vaccine. Contains attenuated viruses that cause these diseases. The vaccine is safe, that is, it is impossible to get sick from it, while immunity is developed.
How to get vaccinations - what mothers need to know
[sc: ads]
Most likely, parents are scared of the likely consequences of vaccinations, among which there are very serious complications:
- Anaphylactic shock;
- Severe allergic reactions (Quincke's edema, Steven-Johnson syndrome);
- Poliomyelitis (after vaccination against poliomyelitis);
- Encephalitis, meningitis, neuritis and other CNS lesions;
- Generalized infection, osteitis, osteomyelitis after BCG vaccination;
- Chronic arthritis after rubella vaccine.
The likelihood of such complications, of course, scares young parents. To reduce the risks of complications, vaccination must be carried out in compliance with all the rules.
Fundamental rules
1. The vaccination schedule is the recommended vaccination schedule for the baby. It can be changed if there are reasons to postpone or completely cancel the vaccine. The cause of temporary medical withdrawal may be:
- Malaise, colds, fever;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Recent blood transfusion;
- Prematurity.
In each case, the duration of medical attention is determined individually, usually a period of from a week to 1 month. Indication for the complete cancellation of vaccination is:
- Allergic reaction to previous vaccination;
- Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
2. The vaccine can be given only after a thorough examination by a doctor. The doctor’s task is not only to examine the child thoroughly, measure the temperature and ask the mother about the characteristics of the baby’s body. Another important point is informing mom about the vaccine itself. The doctor should talk about what vaccine will be given, how it works, what vaccine will be given, what complications are possible after vaccination. Good to know! – Memo for moms how to communicate with a doctor.
3. Mom can choose which vaccine to deliver to the child. In the clinic, all vaccinations are free, but if the parents do not want to put the vaccine that was purchased at the clinic - they can buy their own. Usually this is done if they want to deliver a better imported vaccine or to give a comprehensive vaccine.
4. Store and transport the vaccine only in the cold, at a temperature of 2-8C. This rule applies, first of all, to the situation when the mother buys the vaccine herself, since in the pharmacy and clinic all the rules of storage and transportation are unconditionally observed. When buying a vaccine in a pharmacy, you need to buy a cold element (“snowball”) and take a check. This may be needed in the pediatrician’s office to confirm that the vaccine is fresh and stored correctly.
5. The child herself is vaccinated by a nurse in the treatment room. All data about the vaccine (date, name of the vaccine) is entered on the card. After vaccination, the task of parents is to monitor the condition of the baby and take action if the vaccination gives a reaction. The most common occurrence is a rise in temperature. About how to control the reaction of the child's body and what to do if the temperature rises - read here (link).
Important: How to prepare a child for vaccination - rules, tips and tricks
How to refuse vaccination
[sc: rsa]
Vaccinations are optional, so if parents are against vaccinations for fear of complications, they can write a written refusal. An application can be written by one of the parents in the name of the head doctor of the children's clinic (or maternity hospital, if the refusal of vaccination occurs there). There is no clear application form, but there is a good example of what it should be like:
Statement:
I, (full name), living at: (...) declare that all preventive vaccinations have been refused (including vaccinations against hepatitis B, tuberculosis, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio, hemophilus infection, measles, mumps, rubella) and tuberculosis care for my child (full name) until he is 15 years old.
This refusal is a deliberate decision, and fully complies with the current legislation, including:
1) Art. 32 (on consent to medical intervention) and Art. 33 (on the right to refuse medical intervention) of the “Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on the protection of the health of citizens” dated July 22, 1993 No. 5487-1;
2) Art. 5 (on the right to refuse vaccination) and Art. 11 (on vaccination with the consent of parents of minors) of the federal law of the Russian Federation “On the immunoprophylaxis of infectious diseases” dated September 17, 1998 No. 157-ФЗ;
3) Art. 7, part 3 (on the provision of anti-tuberculosis care to minors only with the consent of their legal representatives) of the federal law “On the prevention of the spread of tuberculosis in the Russian Federation” dated June 18, 2001 No. 77-ФЗ.
I ask you to ensure the preparation of medical documentation for my child in an unconditional order, without requirements for vaccination. In the form 063, please note that there are no vaccinations on the basis of Art.5 and 11 of the law of the Russian Federation "On the immunoprophylaxis of infectious diseases."
In case of your refusal, a copy of this statement and my complaint will be sent to the relevant authorities and organizations to take measures to suppress your illegal actions.
________________ (date) ________________ (signature)
We also read: Is a rise in temperature in a child after vaccination a normal occurrence or an alarm? and useful article aboutIs it possible or impossible to bathe a child after vaccination?
Each family, in its own way, decides on the issue of vaccinations: whether to put or not, buy their own vaccines, or trust doctors from the clinic. The most important thing is that the children are healthy.
Further details:






The eldest son under 6 years old was vaccinated without any particular consequences. But my daughter, at 6 months of age, received 1 vaccination with AKDS + hepatitis + polio and for 7 months we’ve been treating a hypoxic lesion of the central nervous system. Before vaccination, there was a healthy child.
Think brains, mothers. There is a lot of information on the network, for now. Then they will control everything. Do not poison children with mercury that is not excreted with formaldehyde and the like. At least one who asked for a vaccination certificate? Read the composition? Seen how it is stored? Start small though, don't be slaves.
And what to do in a situation where you bring your vaccine, but they refuse to put it in the clinic, sending it to a private clinic. For “we do nothing but our vaccines.” We want to vaccinate against rotavirus, and still nothing. Time is limited, vaccines are bought. They also refuse to pay, they say or you do everything clever right away (which is 8,000 rubles at a time), or go to the children's clinic. Vicious circle.