Twenty-eight days - exactly how long the neonatal period lasts, during which the child’s body undergoes adaptation to completely new conditions for him now in utero, so the reflexes of a newborn baby play a major role here.

This is explained by the fact that a very recently born baby is still deprived of many useful skills - nature takes care of it.
Main reflexes
In this period, the baby only develops unconditioned reflexes - that is, those that are laid as if by default. Gradually, some of them disappear, giving way to conditional ones.
Conditioned reflexes can also be called the "personal experience" of the child, since they are acquired in the process of further development and maturation of the brain.
What are unconditioned (innate) reflexes for?
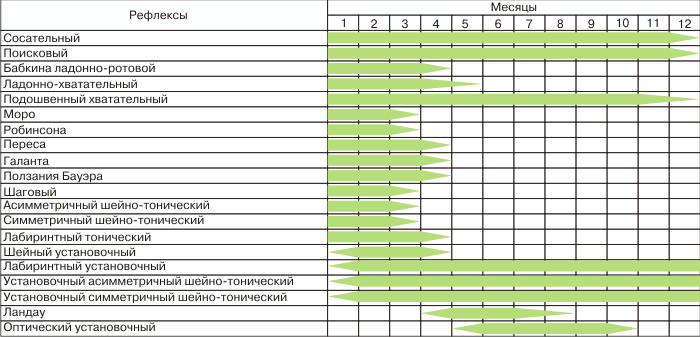
Clinically significant unconditioned reflexes in a baby are as many as fifteen - and their “fate" is very different: some are needed only to survive the difficult process of birth (therefore, they quickly disappear after birth), others to give an impetus to the development of new ones, and still others remain for life.
Pediatric neonatologists subdivide newborn congenital reflexes into several groups:
- Providing general normal life activity (respiratory, sucking, swallowing, as well as spinal reflexes)
- Aimed at protecting the child's body from external influences of bright light, cold, heat and other irritants
- "Temporary" reflexes - for example, the breath-holding reflex, necessary for moving along the birth canal of the mother.
Oral reflexes
The ability to suck a mother’s breast or pacifier on a bottle of artificial nutrition is called sucking reflex, and the ability to swallow the food eaten - swallowing.
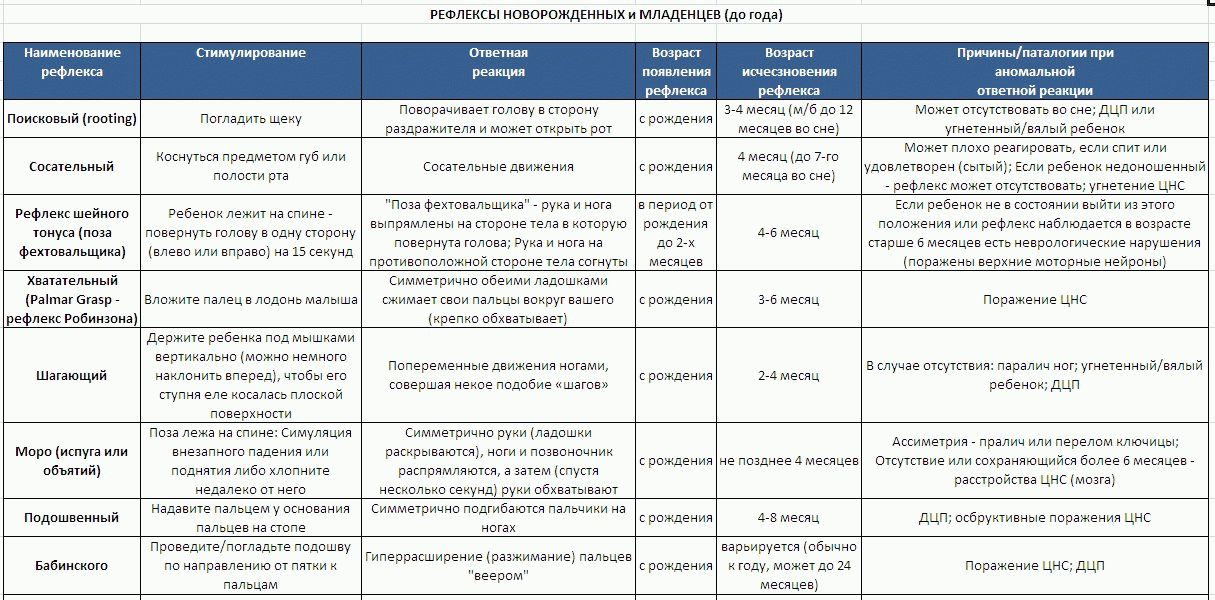
Sucking reflex arises in the first hours of life and lasts up to a year: the baby grips the nipple with his lips, the bottle’s horn and sucks them rhythmically - something like this from the point of view of physiology looks like a normal feeding process. In detail about sucking reflex
Swallowing reflex stays for life.
Proboscis reflex - Another type of oral reflexes. If it is easy to touch the baby’s lips, they funny bulge into a tube - just like the trunk of a baby elephant, because at that moment the circular muscle of the mouth is involuntarily contracted. The proboscis reflex disappears by two or three months.
Reflex Babkin (palmar-oral) - a mixed form of the child’s reaction, in which he opens his mouth if you gently press both palms with your thumbs. It is best expressed in the first two months of life, in the third it begins to fade and then disappears completely.
Kussmaul Reflex (search) - an attempt to find food: if you touch the corner of the child’s mouth, he turns his head to the irritant. It disappears quite quickly - three to four months after birth. In the future, the search for food occurs visually - the baby sees a chest or a bottle.
Spinal reflexes. Examining the baby immediately after birth and throughout the entire period of the newborn, the pediatrician draws attention to the spinal reflexes - A set of reactions responsible for the state of the muscle apparatus.
Upper protective reflex. One of the most important unconditioned reflexes starting in the first hours of life is the upper protective reflex. It manifests itself if you put a newborn baby on his stomach: immediately the head turns to the side, and the baby tries to lift it. This is a protection against possible respiratory failure: in this way, the child restores air to the airways. The reflex disappears one and a half months after birth.
Grasping reflexes
Reflexes of Yanishevsky and Robinson in a newborn child, they appear when he firmly grabs the fingers of the mother (doctor) with both hands and is able to hold them so tightly that he can even be lifted in this way. They are expressed up to three to four months, then weaken. The persistence of these reflexes at a later age is evidence of existing neurological problems.
Babinsky Reflex - it is also called the plantar reflex: lightly stroking the edges of the soles from the outside causes the fingers to open in the form of a fan, while the feet are bent from the back. The evaluation criteria are vigor, and especially the symmetry of movements. One of the most long-lived congenital reflexes - it is noted up to two years.
Other motor reflexes
Reflex Moro - a two-phase reaction in which the child responds to a fairly loud knock on the changing table or any other sharp sound.
- The first phase - the baby spreads its arms to the sides and unclenches the fingers, while straightening the legs.
- The second phase is a return to the previous position. Sometimes a child can even embrace himself, as it were, which is why Moro’s reflex has another name - “hug reflex”.
Pronounced until the age of five months baby.
Reflex Kernig - the reaction of the hip and knee joints to an attempt to release them by force after bending. Normally, this fails. Disappears completely after four months.
Reflex "automatic" gait, which is a very funny sight, consists in the attempts of the newborn to really walk, if you lift it and tilt the body slightly forward. The evaluation criterion is the degree of completeness of support when “walking” the entire foot. Reliance on fingers and clutching of feet for each other is a sign of violations requiring the supervision of a pediatric neurologist.
Reflex support - the baby’s attempt to stand on his feet, when he is gently holding, put on a flat surface (on the table, for example). This is a two-phase reflex: first, the baby, having felt the touch of support, sharply bends the legs at the knees, and then it becomes both feet and firmly presses the soles to the table. Well-defined reflexes of support and “automatic” gait persist for a month and a half.
Bauer Reflex (spontaneous crawling) can be observed by laying the baby on his stomach and putting his palms to his soles: he begins to crawl, starting from the created support and helping himself with his hands. Appearing on 3-4 days, this reflex disappears after 3-4 months.
Galant Reflex - the reaction of the spine to an external stimulus. If you hold your finger along the entire length of the ridge, then the child bends the back, while unbending the leg from the side of the stimulus.
There are also posotonic reflexes newborns - attempts to redistribute muscle tone when the body posture changes in the absence of the ability to hold the head, sit and walk.
Magnus-Klein Reflex - the reaction of the extensor and flexor muscles of the shoulder, forearm and hand, in which the child takes the “fencer's pose”. This happens if the baby's head is turned to the side. You can observe how the arm and leg are straightened from the side where the child’s face is. On the opposite side, they, on the contrary, are bent. This reflex lasts up to two months.
Weak reflexes or when you need to sound the alarm
It happens that some of the baby's reflexes turn on late or do not manifest themselves very clearly. This may be due to trauma received during childbirth, with diseases, as well as to be an individual reaction to certain medications.
Also, weak oral and spinal reactions are usually observed in premature babies and in those born with mild asphyxia.
Interestingly, the weak reflexes in a newborn child associated with the search for food and its absorption (sucking and swallowing) can be explained only by the fact that the baby is simply not hungry. Most clearly they appear before feeding.
The most scary situation is when there are no reflexes at all. The complete absence of reflexes in a newborn baby is a reason for immediate resuscitation, which should be carried out only by specialists.
The reasons for this are different - intrauterine malformations, severe birth injuries, deep asphyxia (strangulation of the umbilical cord).
However, it should be remembered: the reserves of the child's body are huge, so in many cases it is quite successfully restored, and the baby grows up healthy.
Updated:
Often ask a question: What are vestigial reflexes? These are reflexes that disappear over time (up to one year of life), i.e. These are: grasping reflex, Moro reflex, Support reflex, Auto gait reflex, Crawl reflex, Galant reflex, Sucking reflex, Search reflex, Proboscis reflex, Palmar - oral reflex.
We also read:
- 15 abilities (reflexes) of the newborn, helping him to survive and develop
- Child development up to a year by months
- Daily and weekly childcare from birth to year
- How to start hardening a newborn baby. Rules and methods of hardening
- Massage the baby in 1 month
Video Consultation: Newborn Reflexes
Celekhovich Olga Petrovna - a doctor of the highest category tells what basic unconditioned reflexes should be normal in infants.






Hello!
Congenital (and in older children too) reflexes from nature (intuitive) not only for communication with the outside world but also for the resolution of internal anxieties and ailments, protection from external influences.
Therefore, it is possible to successfully apply children's reflexes to adults to treat various diseases.
Unfortunately, as we grow older, public order erases them and, as a result, a person remains without natural protection.
For example: cry and laugh. In many places and situations (especially for men) it is considered not eligent.
I will be glad to find like-minded people 🙂