 One of the external indicators of the normal development of the child for pediatricians, neurologists and other children's specialists is the fontanel in newborn children. It is a small soft pulsating area on the baby’s head, under which brain tissue is located fairly close. The fontanel surface is covered with a dense film with a small fluff.
One of the external indicators of the normal development of the child for pediatricians, neurologists and other children's specialists is the fontanel in newborn children. It is a small soft pulsating area on the baby’s head, under which brain tissue is located fairly close. The fontanel surface is covered with a dense film with a small fluff.
Fontanel of a newborn baby
- The fontanel of the newborn greatly facilitates the process of childbirth, both for the baby and for the mother. Passing through the birth canal, the bones of the skull are compressed, and therefore the head of the newborn for the first time after birth looks elongated. Then the shape of the head is restored;
- The presence of a fontanel provides optimal spatial conditions for normal brain growth at a pace that is laid by nature;
- The fontanel is involved in the regulation of heat transfer between the baby and the environment. If the child’s body temperature exceeds 38 degrees, then brain tissue naturally cools through the fontanel;
- Due to the ability to compress, the fontanel can serve as a shock absorber in case of accidental fall of the child.
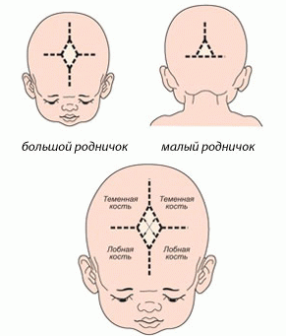
Where is
Determining where the fontanel is located in a newborn baby is quite simple.
A large fontanel in the form of a rhombus measuring 2 by 2 centimeters is located directly in the middle of the crown of the head, or, as usual, they say - on the top of the head.
A small fontanel is located at the back of the head. Its size is about half a centimeter.
When it overgrows
A large fontanel overgrows by about a year old child, sometimes there are small deviations from this parameter up to about a year and a half. But if the child complies with age standards in other parameters, then there is no reason for concern.
The small fontanel in children born on time is already closed. However, it happens that it was discovered after childbirth. Then its closure should be expected in two to three months.
The speed and time of closing fontanelles mainly depends on how much the baby's body is provided with calcium. If there were no deviations in the mother’s diet, the optimal multivitamin regimen was observed, then fontanel overgrowth usually occurs normally.
Developmental abnormalities
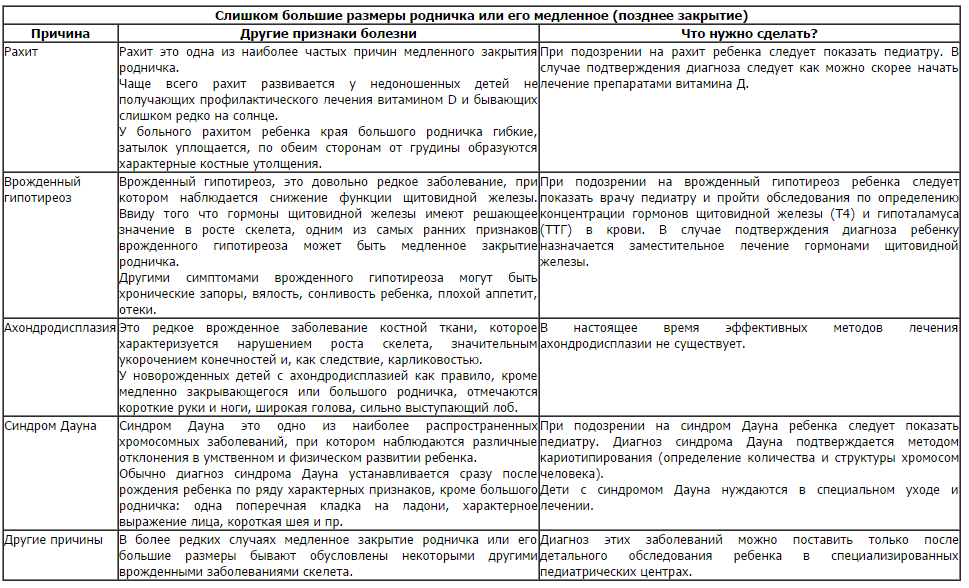
Knowing the timing when the fontanel overgrows, as well as the size, you can see any deviations, avoid and prevent the development of many dangerous diseases in newborns. Among them are several:
- Rickets. This disease is almost the most common cause of late closure of the fontanel. Typically, this occurs in premature infants, rarely in the sun, having a lack of calcium and vitamin D. Read the article about rickets >>>;
- Hypothyroidism A decrease in the number of thyroid hormones can also cause a slowdown in the process of overgrowth of the fontanel;
- Down Syndrome. Too large fontanel sizes indicate the presence of this disease along with other characteristic signs;
- An overgrown fontanel may indicate an excess of calcium, and also testify to diseases such as craniostenosis, microcephaly;
- An indented fontanel is also a serious symptom. This phenomenon indicates acute dehydration.
(the picture is clickable)
A careful examination of the child by specialists, a detailed description by the parents of the state of the baby will be the key to early detection of deviations and will contribute to the correct appointment of preventive treatment.
Causes of early fontanel closure
(clickable)

Bulging fontanel?
Most often, a bulging fontanel is observed against a background of diseases that are accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure: meningitis, encephalitis, tumors, intracranial bleeding, increased intracranial pressure for another reason.
If a bulging fontanel is combined with one or more of the following symptoms, you should call a doctor as soon as possible:
- High temperature;
- The fontanel swelling arose after a head injury, a fall of the child;
- Vomiting
- Drowsiness or excessive irritability of the child;
- Strabismus;
- Cramps or epileptic seizures;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Swelling of the fontanel for a long time without other symptoms.
The fallen fontanel?
Most often, a fontanel sinking is observed due to dehydration of the child against the background of temperature, diarrhea, repeated vomiting. If a sunken fontanel is found, the child should be given plenty of water and contact a doctor to treat the disease that caused dehydration.
Fear of damage
Many are very much afraid of somehow damaging the fontanel. Remember! - this is almost impossible. Despite the apparent softness of the fontanel, it is very durable, and it can not be damaged by the usual manipulations (washing, bathing, combing, etc.).
Video:






If the pediatrician after the examination was diagnosed that the newborn has a fontanel that is too large, you need to pay close attention to the child, carefully monitor him, do not let him cry for a long time, supplement the menu of the nursing mother with foods high in calcium and vitamin D.
All parents should at least understand a little what constitutes a fontanel in newborns in order to reduce their own feelings when a pediatrician touches their child’s fontanel and understand in timewhen changes in the body of their child are not quite typical and require early intervention by doctors.