The normal functioning of the speech apparatus is as important for the development of the child as the ability to fully move and move. If stuttering occurs, there is a huge danger that your baby will not only be slower than the rest of the children in learning about the world around him, but also become more detached and withdrawn. If you notice the first signs of stuttering in your child, do not let the situation drift.
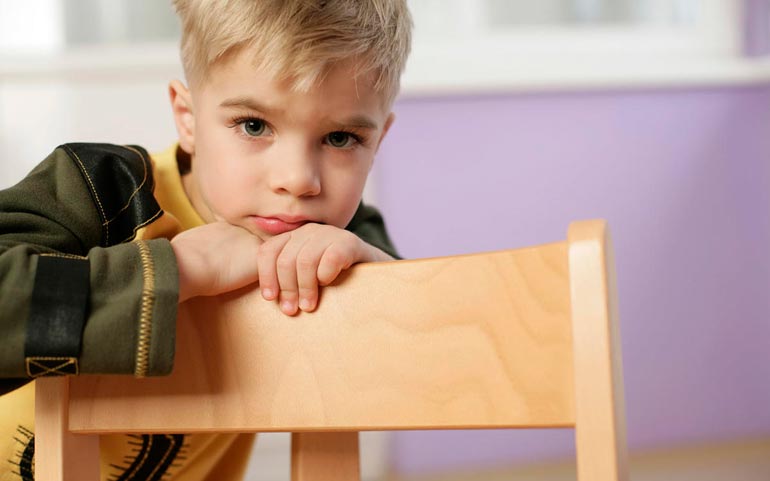

Stuttering — it is a speech disorder characterized by frequent repetition or prolongation of sounds or syllables, or words; or frequent stops or indecision in speech, breaking its rhythmic flow. The diagnosis is made when these symptoms are significant. A more simple, but only generalizing the previous, definition of stuttering as “violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech due to the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus” has been established in Russian speech therapy literature.
First signs of stuttering
When stuttering, almost all children behave the same. The main task of parents is to recognize the first alarm bells in time and prevent the further development of the problem. The main signs of stuttering include the following behavioral features:
- Stuttering is almost always accompanied by tension, anxiety and fear of speech;
- When stuttering, unnatural movements, grimaces of the face or tics are possible, with the help of which a stuttering person tries to overcome stuttering;
- A child can pronounce the first syllables for a long time or repeat the same word several times;
- The child cannot concentrate for a long time, suddenly breaks off his speech, falls silent;
- At the beginning or in the middle of a sentence, between the words the extra sounds “A”, “O”, “And” are often repeated;
- The child often stops and thinks over every word;
- Superficial, irregular, clavicular or chest breathing, respiratory discoordination. The baby begins to speak after a full breath or while inhaling;
- Involuntary movements during speech - blinking, bloating of the wings of the nose, twitching of facial muscles;
- The use of speech tricks to hide the defect - smile, yawning, coughing;
- The kid begins to use gestures instead of words.
Stuttering occurs regardless of age, but most often occurs in children aged 2 to 6 years, when speech skills are developed. Boys are three times more likely to stutter than girls. Sometimes a relapse of stuttering occurs in adolescents aged 15-17 years, most often this is due to the occurrence of neurosis.
Psychological features of stuttering
- timidity and embarrassment in the presence of people;
- excessive sensitivity;
- fantasy brightness enhancing stuttering;
- relative weakness of will;
- a variety of psychological tricks to eliminate or reduce stuttering;
- fear of speaking in the presence of certain people or in society.
Consequences of stuttering
- Violation of social adaptation;
- Decrease in self-esteem;
- Logophobia - fear of speech;
- Soundophobia - fear of making a separate sound;
- The aggravation of speech impairment.
Causes of stuttering
Stuttering may appear quite unexpectedly. But in every case, any type of stuttering has its own reason for appearing. It is this reason that must be found as soon as possible, since it will depend on this further success of the treatment.
- Fright
- Transferred meningitis or encephalitis;
- Diabetes;
- Frequent insomnia and enuresis;
- Lack of exercise and fatigue;
- Long stay in a stressed neurotic state;
- A sharp change in environment (moving, long journey);
- Excessively strict attitude of parents to the child;
- Disturbances in the central nervous system;
- Heredity;
- Bruised head, concussion;
- Poor adaptability to society;
- Excessively late or excessively early development of speech;
- Violation of the normal functioning of the central nervous system;
- High susceptibility to colds.
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish 2 main types of stuttering:
- Neurotic - occurs due to a psychological trauma, shock (for example, fright or stress; this form of the disease is usually easy to correct) or due to an excessively increased speech load. This type of disorder affects mostly impressionable and vulnerable children.
- Neurosis-like - often develops with damage to the nervous system, which can be inherited or become a consequence of a violation of intrauterine development.
By the nature of seizures, stuttering occurs:
- Tonic, associated with a sharp hypertonicity of the muscles of the lips, tongue, cheeks, leading to a pause in speech.
- Clonic - characterized by multiple contraction of articulation muscles, and leads to the repetition of a single syllable or sound.
- Tonic-clonic.
- Clone tonic.
- Articulatory.
- Voice
- Respiratory.
- Mixed.
Seek help from a specialist immediately after you notice signs of stuttering in the baby. In the early stages, the problem can still be fixed quickly. Therefore, do not postpone going to the doctor for later, the doctor will help determine the type and type of disorder, as well as prescribe effective treatment.
Why does the child stutter:
Help child
In the presence of stuttering, it is necessary to visit several doctors at once, namely speech therapist, psychologist, neurologist. After a full examination and excluding symptoms that are not related to the disorder, you can begin full treatment.
With the neurotic type of stuttering, the doctor prescribes special therapy, which should reduce exposure to stress and violent emotions. This will help to find an appropriate approach to the child and teach parents to communicate with him correctly.
With neurosis-like stuttering, medication is necessary, combined with a visit to a psychologist. In order for the result to be noticeable and sustainable, long-term treatment is necessary, which will be accompanied by maintaining comfortable conditions in the place where the child lives.
When treating stuttering, it is necessary to adhere to the following doctor's recommendations:
- Create comfortable conditions for the child in the house. Make sure that the baby does not get out of balance and does not provoke negative emotions, exclude cartoons and games of an aggressive nature;
- Pay special attention to the calm atmosphere in the family - the child should not hear screaming, quarrels, experience punishment, see sudden movements and gestures;
- Communicate with the baby in calm tones, speak clearly and legibly;
- Never tell a child that he is saying or saying something wrong;
- Read more tales for your child (the effect of fairy tales on a child)Do not read terrible tales at night, as this provokes a feeling of constant fear: fear of seeing Baba Yaga, hell, the devil;
- Get in the house pet. Thus, the baby will cease to feel lonely and depressed, and will make a real friend;
- Speak with the stutter clearly, fluently (without breaking one word from another), take your time, but do not pronounce words in syllables or in a chant;
- Try to bring the baby closer to the balanced, well-speaking peers so that he learns to speak clearly and expressively;
- You can not involve a stutter in a game that excites and requires speech participants from participants;
- If the kid does not want at some point to communicate with people or with his peers in the playground, do not force him to this.
Older children need deeper treatment, which includes the prevention of personality distortion. This therapy is carried out by a psychologist so that the baby does not feel restless and does not experience complexes due to his problem. If you do not resort to this therapy, then the child may develop a fear of talking and being surrounded by people.
Preventative measures
To prevent the development of a possible stutter or consolidate the effect after treatment, it is necessary to follow the following preventive measures:
- Create for your baby the ideal mode of the day, in which he will have enough time for games, walks and sleep. At the age of 3 to 7 years, the child needs at least 10 hours of nighttime sleep and 2 - daytime sleep. Daytime sleep is simply necessary, because it positively affects the psycho-emotional state of the baby.
- Do not allow to watch programs and cartoons that do not correspond to the age category of your child and can cause unpredictable emotional outbursts.
- Do not overload the baby with new impressions (reading, movies, watching TV) during the period of remission after treatment.
- Do not overload the child, forcing him to learn whole poems by heart to show off to friends or parents in the kindergarten.
- When punishing a child, do not leave him alone in a dark room, as there is a high risk of developing obsessive fear. Better leave the baby without a sweet or without a favorite toy if he is guilty.
- Involve your child in music or dance classes, this helps to establish the correct speech breathing, rhythm, pace, and so, the baby will be liberated and become more confident in himself. Useful singing classes.
[sc name = ”ads”]
Stuttering in children is a serious enough problem, but completely eliminated if you pay attention to it in time and go to the right specialist for help.
What should I do if the child starts to stutter?
SDK: Speech Therapist Class: Stuttering
Dr. Komarovsky, along with speech therapist Victoria Goncharenko, will find out how parents should act if their child has a speech disorder: which doctor to go to, what day regimen to choose, what to do with the baby. Also, Evgeny Olegovich and his guest will answer questions from the audience by describing the behavior of parents with children who have stuttering.







My daughter began to stutter from the age of 7. And it’s somehow strange: only when he is in a hurry to say something. Please speak more slowly - stuttering disappears. We are trying to develop diction. Speech has become a little better.
Unfortunately, the reason for stuttering in children may be the attitude of parents, and not just the one stated in the article. Of course, this can be attributed to neurosis, but if a child is beaten at home, screamed at him, and scolded, then a persistent fright develops, which can entail, unfortunately, stuttering.
It seems to me that if a child is already stuttering, then first of all it is necessary to ensure that he is not very shy about this and does not worry about this. It is worth explaining that this can be fixed, otherwise the baby will close even more and it will be more difficult to overcome the problem.
My son at the age of five noticed a stutter, even somehow unexpectedly. They decided that something scared him. Fortunately, everything was noticed at an early stage, and a child psychologist and speech therapist helped to cope, so far no relapses have occurred.
My son stuttered after a dog attacked him in the yard. The child was very scared, it’s good that she didn’t bite, she simply barked at him. We turned to a child psychologist. He studied with him for two months, after which the results immediately became noticeable. And the stuttering passed, and the fear of the dogs is no more. The main thing is to take control of the situation on time.